Chemical Nature Of Crude Drugs: Alkaloids
Chemical Nature Of Crude Drugs.
Alkaloids
- Definition: Alkaloids are basic nitrogenous organic compounds of the plant origin, having marked physiological action when taken in the small dose and containing one or more than one nitrogen in a heterocyclic ring.
- Physical Properties:
- They are colorless crystalline, non – volatile & bitter in taste.
- They are solid, insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents.
- Generally, they are levorotatory.
- There are some exceptions Coniine is dextrorotatory. Nicotine is liquid and Berberine is yellow.
- Alkaloids found as salts of organic acids in the plant.
- Biological Role: -
- 1) They protect the plant from insects and animals
- 2) They take part in protein synthesis.
- 3) They stimulate and regulate growth, reproduction & metabolism of the plants.
- 4) They are detoxicating agents.
- 5) They act as a nitrogen reservoir for the plant.
- Identification Tests: -
- There are two types of tests.
- 1) Precipitation tests.
- 2) Colour tests.
- Precipitation tests:-
Mayer’s Test
|
Alkaloid + Mayer’s reagent
(Mayer’s reagent: Potassium mercuric iodide solution)
|
Cream Color or ppt
|
Dragendorff’s Test
|
Alkaloid + Dragendorff’s reagent
(Dragendorff’s reagent: Potassium Bismuth iodide solution)
|
Brown or reddish Brown ppt. Or colour
|
Wagner’s Test
|
Alkaloid + Wagner’s reagent
(Wagner’s reagent: Iodine & pot. Iodide solution)
|
Brown or reddish brown ppt or color.
|
Hager’s Test
|
Alkaloid + Hager’s reagent
(Hager’s reagent: Saturated solution. of picric acid)
|
yellow ppt.
|
- Colour Tests: -
- a) Potassium chlorate + Caffeine + a drop of HCl – It gives a purple color.
- b)Colchicine + HNO3 – yellow color.
CLASSIFICATION OF ALKALOIDS:-
- Alkaloids can be classified by two methods:
- 1) Classification based on pharmacological actions.
- 2) Classification based on a chemical nucleus.
- 1) Classification based on pharmacological actions:
- Antimuscarinic: Atropin, Hyoscine.
- Anthelmintic: Emetine.
- Anticancer: Vincristine, Vinblastine.
- Adrenergic: Ephedrine.
- CNS Stimulants: Caffeine, Strychnine.
- Analgesics: Morphine, Codeine.
- 2) Classification Based on a chemical nucleus:
Types of alkaloids
|
Example
|
Sources
|
1. Tropane.
|
||
2. Quinoline.
|
Quinine, Quinidine
|
Cinchona
|
3. Isoquinoline.
|
Papaverine, Emetine
|
Opium, Ipecac
|
4. Indole.
|
Strychnine, Brucine, Reserpine
|
Nux-vomica, Rauwolfia, Vinca
|
5. Phenanthrene.
|
Morphine, Codeine
|
Opium
|
6. Purine.
|
Caffeine
|
Tea, Coffee.
|
7. Pyrrole and pyrrolidine.
|
Nicotine
|
Tobacco
|
8. Pyridine and Piperidine.
|
Coniine, Lobeline
|
Hemlock, Lobelia.
|
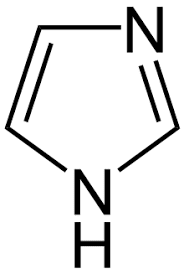
9. Imidazole.
|
Pilocarpine
|
Pilocarpus.
|
10. Steroidal.
|
Conessine, Solanin
|
Kurchi, Potato.
|
11. Terpenoids.
|
Aconitine
|
Aconite
|
12. Alkaloidal Amines. (Protoalkaloids)
|
Ephedrine, Cholchicine
|
Extraction of Alkaloids
- Method of Isolation depends upon chemical nature of Alkaloid
- Method I
- 1) The drug is powdered & extracted with ethyl alcohol.
- 2) Remove the solvent by evaporation.
- 3) Treat the residue with water.
- 4 )Separate the water containing free bases.
- 5) Add sodium carbonate & extract the solution with Ether.
- 6) Evaporate the Ether to obtain crude product.
- 7) Pure these alkaloids by chromatography.
- Method II:
- 1) Powder of drug is treated with water & lime.
- 2) The lime combines with acid, Phenolic substances, & tannins.
- 3) The powder is extracted with ether.
- 4) The ether is shaken with water & alkali.
- 5) The impurities go in ether solution.
- 6) The crude alkaloids come in aqueous soln.
- 7) This solution is again extracted with chloroform to obtain pure alkaloids.
Labels: Pharmacognosy













<< Home